Last time, we looked at the Meio Coup that saw the Shogun’s kanrei (deputy), Hosokawa Masatomo, take over the government and install a puppet Shogun with himself in effective control. At the end of that post, we also looked at how, despite the coup’s success, Masatomo’s grip on power was far from secure.

As soon as the dust settled, Masatomo found himself surrounded by problems. Some had been long-standing, violence between powerful clans in the provinces had been a problem for decades, and Shogunate authority outside of Kyoto was tenuous at best.
Within Kyoto, too, there were enduring rivalries between different factions, sometimes within the same family, all revolving, as it always had, over who would control the throne, or the man (it was always a man) sitting on it. In many ways, Masatomo’s coup can be seen as a continuation of political instability that went back centuries. As long as there had been an Imperial Throne (nearly a thousand years at this point), there had been powerful families vying to control it. That situation hadn’t really changed when the centre of power became the Shogun instead of the Emperor.
Some of the problems were of Masatomo’s own making, though. He was, but most contemporary accounts describe him as an authoritarian and quite eccentric character. It is easy for us to imagine the Shogun as some all-powerful ruler, but the reality was that there was a considerable amount of power sharing in the capital. This was no democracy, but it was also expected that the powerful clans surrounding the throne would be consulted about government matters and have their seat at the table when it came to running things.
There had been several examples of powerful families coming to dominate the government, and again, Masatomo was just continuing that trend, but like the families who came before him, centralising all power in one man attracted a lot of hostility from the other clans who now found themselves frozen out.
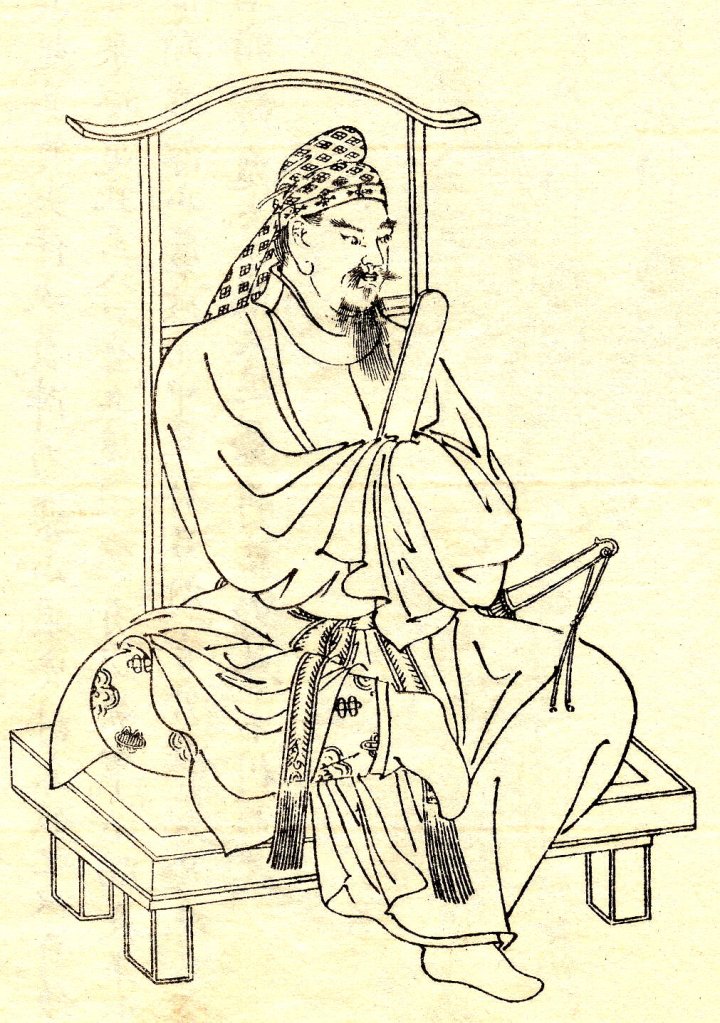
The other problem with Masatomo was that he was something of an eccentric iconoclast. A follower of the ascetic Shugendo sect of Buddhism, he lived an austere life, swearing off certain foods, all alcohol and the company of women, though some contemporary sources suggest his aversion to sex wasn’t limited to his male companions, and he was apparently a practitioner of shudo, a kind of ritualised homosexuality that was common amongst Samurai.

By 唐山健志郎 (Kenshiro Karayama) – 唐山健志郎 (Kenshiro Karayama), CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=2259089
Masatomo is supposed to have believed that his religious fervour would allow him to engage in magical feats, such as being able to fly or speak mystical languages. He had more practical eccentricities as well; he would go on long journeys, sometimes alone, and without telling his retainers, meaning that government would effectively come to a halt until he could be found.
Religious and sexual habits aside, Masatomo also opposed much of the pomp and ceremony surrounding the institutions of government. It is said that he disliked the formal clothing required at certain ceremonies, and the official enthronement of the new Shogun was delayed simply because Masatomo refused to wear the eboshi hat required by tradition.

Masatomo also had a shockingly (for the time) rational approach to the Imperial Court as well. He is supposed to have opposed the enthronement ceremony of Emperor Go-Kashiwabara on the grounds that, since the Emperor no longer had any real power, there was no point in a grand ceremony. This was technically true, but flew in the face of long-established tradition.
So a combination of Shogunate weakness, Political problems, and personality issues meant that Masatomo’s position was never strong, and he wouldn’t help matters with some of the decisions he made. Given Masatomo’s apparent aversion to women, he wasn’t able to produce an heir (obviously). This problem wasn’t an uncommon one at the time, and adoption was usually the preferred solution.
Masatomo, never one to do anything the easy way, adopted three sons, Sumimoto, Sumiyuki, and Takakuni. You may remember, in the period leading up to and including the Onin War, one of the key factors in the instability that gripped the realm was the frequency of internal conflict over clan succession. One of the reasons the Hosokawa Clan had been able to take such a strong position was that they had largely been able to avoid these struggles, with Masatomo succeeding his father relatively smoothly.
Some contemporary sources suggest that Masatomo’s ultimate plan was to divide the Hosokawa lands between two of these sons, while the third would inherit the position of kanrei and thus real political power. Initially, it seems that Masatomo favoured Sumimoto to succeed him as kanrei, but the fact that all three ‘sons’ came from three different families meant that the succession was now the subject of growing factional rivalries.

This situation was precarious, but held together by the sheer force of Masatomo’s will. With power centralised in his hands, he could exert enormous control over what remained of the Shogunate government and its nominal loyalists. This way of doing things required him to be alive, however, which he no longer was after June 23rd, 1507, when he was assassinated.
The assassins were apparently partisans of Sumiyuki, favouring him as kanrei over Sumitomo, who they also attacked at the same time as his father, though Sumitomo was able to escape with the help of his supporters, led by members of the Miyoshi Clan (a name that will become important later).
The fact that Sumitomo survived was a problem for Sumiyuki, especially after he fled to Takakuni, the third brother, who agreed to support him and march against Sumiyuki. There was a series of blood battles between the rival factions until Sumitomo’s supporters, led by Miyoshi Yukinaga, took his final refuge at Yushoken, forcing Sumiyuki to commit suicide.

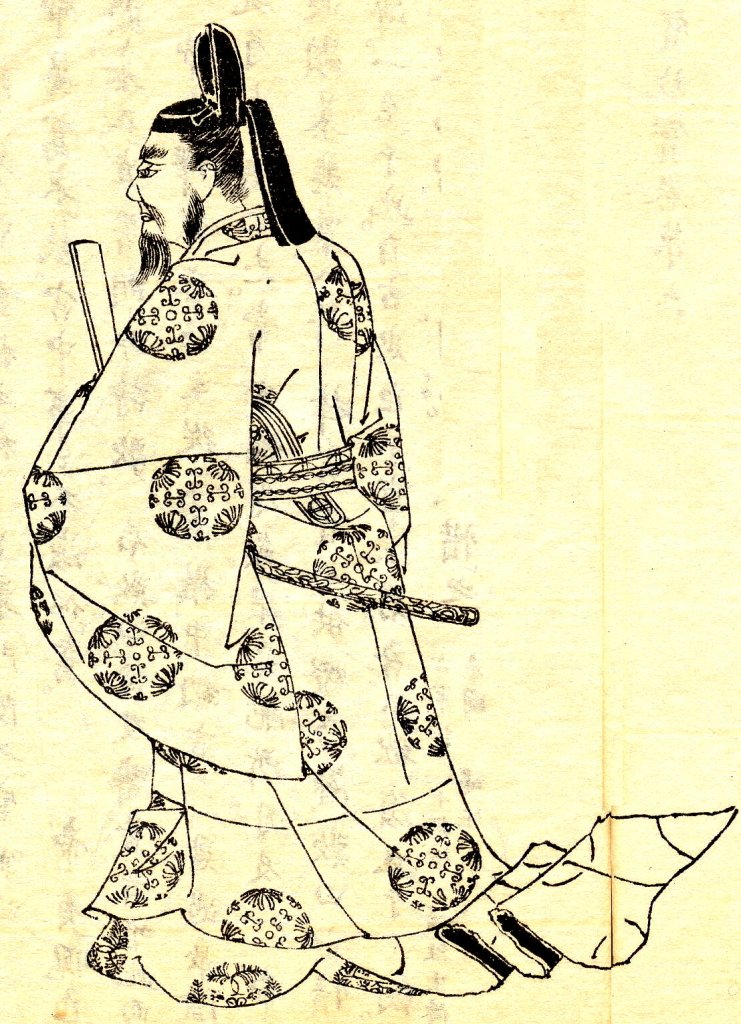
Musuketeer.3 – 投稿者自身による著作物, CC 表示-継承 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=24893374による
It turns out that your enemy’s enemy isn’t always your friend, though, and it wasn’t long before Takakuni and Sumitomo were at each other’s throats. The problem stemmed from Sumitomo’s supporters amongst the Miyoshi Clan, whose strength and growing overbearingness earned them many jealous rivals. Then, in late 1507, former Shogun Yoshitane (who had fled after the Meio Coup) returned to the scene.
Yoshitane, after fleeing into exile, had been supported by the Ouchi Clan based in modern-day Yamaguchi Prefecture, and now they raised their banners in support of his march on Kyoto. Although not strong enough to take the city at first, shortly after the new year, Takakuni became the focal point for anti-Miyoshi feeling and chose to throw in his lot with the old Shogun.
This combined force attacked Kyoto and took the city in early April, forcing Sumitomo and Shogun Yoshizumi to flee. Takakuni was recognised as the new head of the Hosokawa Clan, and Yoshitane was reinstated as Shogun, beginning his second reign.
Sumitomo and Yoshizumi were down but not out, however, and what followed was more than 20 years of strife that is collectively called the Hosokawa Civil War, or Hosokawa Rebellion. This conflict had all the hallmarks of the internal violence that had wracked multiple clans throughout this period, but wrought on a massive scale, involving not just the Hosokawa but their vassals, retainers, and the Shogunate itself.
Sources
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E6%B0%B8%E6%AD%A3%E3%81%AE%E9%8C%AF%E4%B9%B1
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E7%B4%B0%E5%B7%9D%E9%AB%98%E5%9B%BD
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E4%B8%89%E5%A5%BD%E4%B9%8B%E9%95%B7
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E7%B4%B0%E5%B7%9D%E6%BE%84%E4%B9%8B
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E7%B4%B0%E5%B7%9D%E6%94%BF%E5%85%83