Just a quick note from me: Due to real-life changes with workload, I’ve decided to reduce the number of blog posts to one per week. Going forward, the blog will be posted on Fridays.
In 1589, the Hojo openly defied Toyotomi Hideyoshi’s peace orders, prompting the new regent to declare them in rebellion against the throne. (Side note, Hideyoshi, as the son of a peasant, couldn’t be declared Shogun, so he took the title of Kampaku, officially the chief advisor of the Emperor, but in reality, the political master of Japan.)

There were some final (and quite half-hearted) attempts at negotiation, but Hideyoshi’s position was clear: either the Hojo would submit, or they would be destroyed. The Hojo, an old, proud, and powerful clan, refused to bow, and by 1590, Hideyoshi had mustered an army of some 200,000 men to force the issue.
Tokugawa Ieyasu, whose lands lay between the Hojo and Hideyoshi, initially sought to mediate, as his daughter was married to Hojo Ujinao, the nominal lord of the clan. These attempts failed, however, and Ieyasu threw in his lot with Hideyoshi, making preparations in his lands for the movement of thousands of troops advancing on the Kanto.
The Kanto is surrounded by mountains and, at least in theory, very easy to defend, as there are only a limited number of passes through which a large body of troops can pass. The Hojo knew this and fortified as many of these passes as they could. Unfortunately, they were now being attacked on practically all sides. As well as the Tokugawa-Toyotomi force coming from the east, they also face an army sent along the Nakasendo road to attack Usui Pass in the north, and a force dispatched from the North-East would advance into Musashi Province and attack the castles there. Even the ocean to the south wasn’t open to the Hojo, as a naval force attacked Nagahama Castle in Izu.
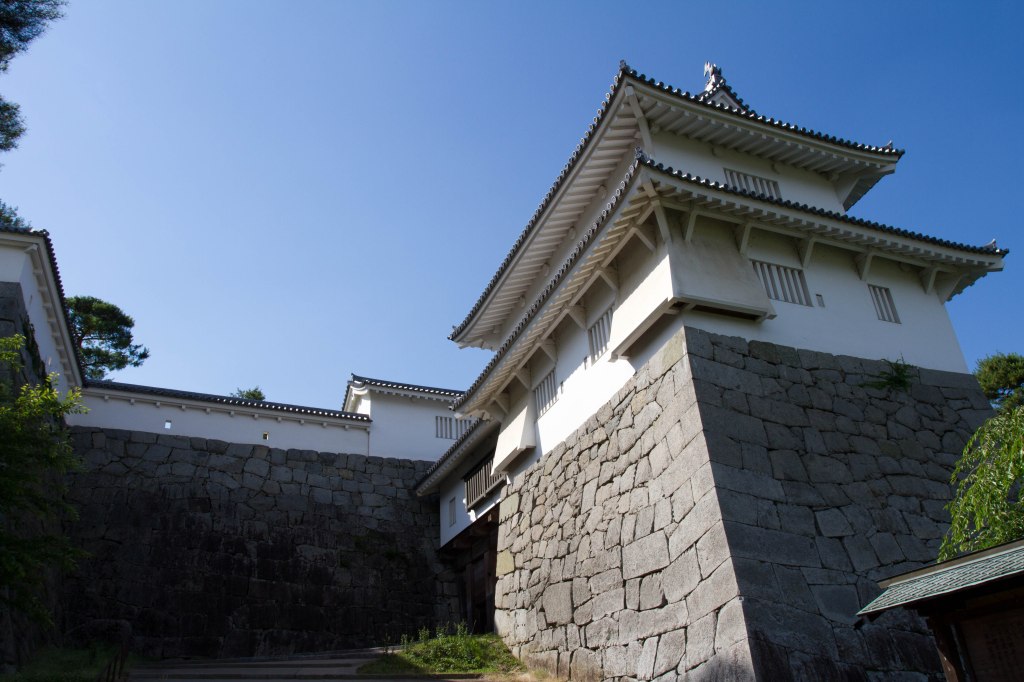
The main blow would come from the west, however, as Hideyoshi led his army in an attack on the apparently formidable fortress of Yamanaka. Before the outbreak of hostilities, the Hojo had dispatched a garrison of 4000 men to the castle and set about improving its fortifications. Unfortunately, this work was not completed by the time Hideyoshi’s army arrived, and, despite its reputation as the “gateway” to the Kanto, Yamanaka fell in a single morning, despite brave resistance from the overmatched garrison.
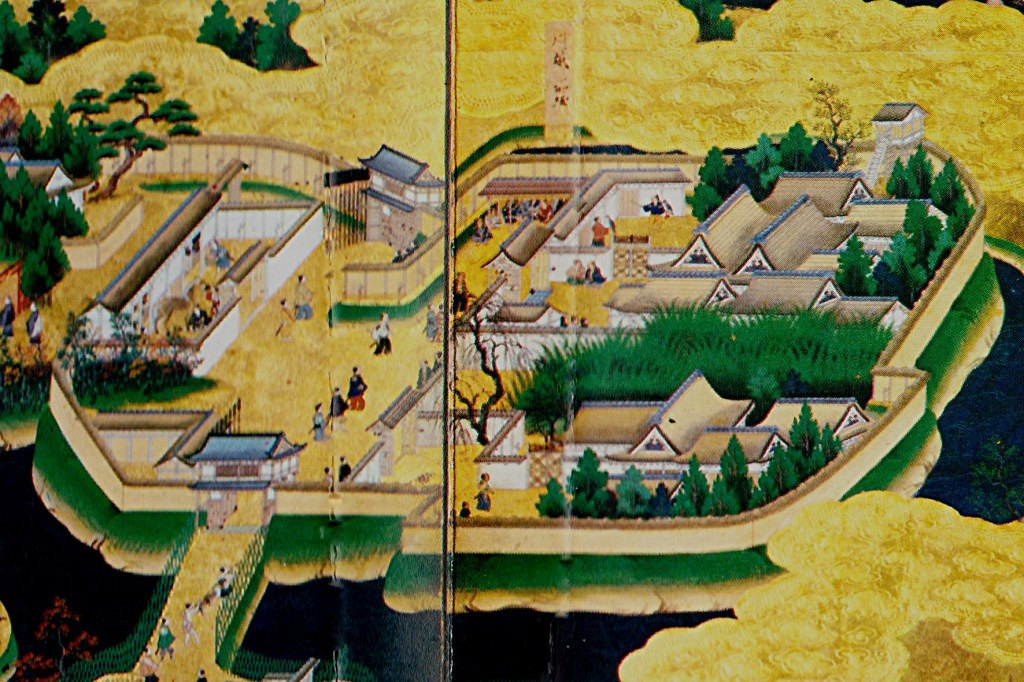
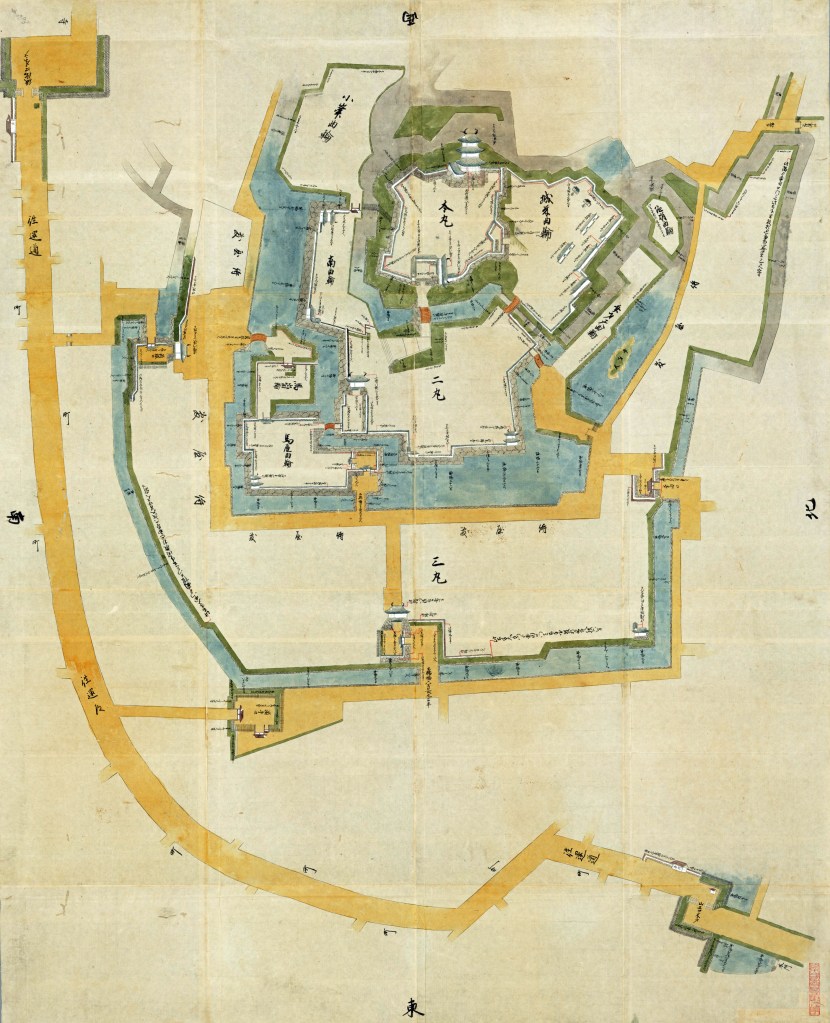
Other castles in the area were taken or besieged, bottling up their garrisons and preventing them from supporting the main attack on Odawara, which itself came under siege in early May. Odawara itself was an enormous castle, and despite the size of Hideyoshi’s army, there was no serious attempt to take it by storm. Instead, the siege camp became something of a small town, with everything from prostitutes to theatrical troupes plying their trade amongst the besiegers, whilst the Hojo defenders were often obliged to sleep on the battlements in their armour, for fear of a sudden attack.
With Odawara now firmly under siege, Hideyoshi was confident enough to dispatch forces to support the campaigns in other parts of Hojo territory, with many of the castles falling with surprising speed. This was largely due to the fact that the Hojo had mobilised the vast majority of their forces for the defence of Odawara itself, leaving most of the outlying castles only lightly defended. When faced with the overwhelming strength of the forces arrayed against them, most of these castles surrendered immediately, or else were taken after only brief resistance.
There is some evidence that the speed at which many of these castles fell led Hideyoshi to criticise his generals in the region, suggesting that taking so many castles so easily could not be considered a military achievement.
The ease of the advance wasn’t true everywhere, however. At Iwatsuki (in modern Saitama), a force of 20,000 was held up by the defenders for several days despite a numerical advantage of 10-1. When the castle fell, Hideyoshi ordered that all the fighting men be killed, and the women and children taken prisoner. Instead, the commanding general, Asano Nagamasa, had already agreed to spare the surviving warriors, the women and the children as part of the surrender agreement.
Meanwhile, the Siege at Hachigata Castle (also in Saitama) concerned Hideyoshi enough that he sent a sternly worded letter to Nagamasa, ordering him to focus his efforts there. Nagamasa did so, and a combined army of some 35,000 men attacked Hachigata, forcing the garrison to surrender. Once again, arrangements were made to spare the garrison and non-combatants, though this time it doesn’t seem to have been in defiance of Hideyoshi’s orders.

Taketarou – 投稿者自身による著作物, CC 表示-継承 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1273726による
While most castles were taken by force, negotiation, or a combination of the two, some held out, either through the skill of their defenders or, as was the case at Tatebayashi Castle, by apparently divine intervention. The castle was apparently founded with the help of a grateful fox, who rewarded the lord of the castle for rescuing its baby by marking out the foundations of the fortress in an area of swampy ground.
This soggy position made the castle very difficult to approach, and when it came under siege, the attackers laid down logs across the swamp to create a roadway to the castle walls. With their pathway secure, the besiegers got a good night’s rest and prepared for a dawn attack. When the sun rose, they found that the roadway had disappeared completely, something put down to the fox spirit protecting the castle rather than the possibility that the logs had just sunk.
Another famous, watery siege was that of Oshi Castle. Surrounded on two sides by rivers, Oshi was besieged by forces led by Ishida Mitsunari (who will become very important). Much ike Tatebayashi, Oshi’s watery position made it difficult to overcome. Mitsunari (apparently on written instructions from Hideyoshi) set about building an enormous levee surrounding the fort, forcing the water from the two rivers to inundate the castle and flood out its defenders.

京浜にけ – 投稿者自身による著作物, CC 表示-継承 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=100409931による
To the besiegers’ surprise, the waters didn’t actually flood the castle; instead, they gave it the appearance of floating on the water, leading it to be referred to as the “Floating Castle” (this is the title of a manga and its later 2012 adaptation, both about the siege). Following several days of heavy rain, the levee broke (or was sabotaged in some sources), flooding the siege camp and killing up to 200 warriors.
The failure of this approach would seriously damage Mitsunari’s military reputation (some sources point out that he was just following Hideyoshi’s instructions, but the damage was done), and the siege was eventually taken over by Asano Nagamasa. An all-out assault on the castle was impossible due to the effects of the flooding, which had turned the ground into an impassable quagmire, and Oshi has the distinction of being one of the few fortresses that held out until the end of the Odawara Campaign, before eventually surrendering nearly 2 weeks after the fall of Odawara.
Odawara, as one of the most formidable castles in the realm, hadn’t come under direct attack, but the siege had been dragging on for weeks, and news from other parts of the Kanto was almost universally bad, sapping the already fragile morale of the defenders. Shortly after the siege began, the loyalty of the Date Clan was still in doubt, and the Hojo held out hope that they might receive aid from outside the Kanto. Date forces indeed entered the Kanto, but in support of Hideyoshi, ending any hope of relief.

Though no general assault was launched, there were a few small-scale skirmishes and sporadic gunfire, and by early summer, signs of a breakdown in morale were appearing on both sides, with an increase of desertion amongst the besiegers, and the ever-present possibility of defection from the Hojo, especially as news of the rapid fall of other castles arrived.
Negotiations began early in the siege, largely facilitated by Tokugawa Ieyasu, Hojo Ujinao’s father-in-law. Rumours of a peace agreement spread almost immediately, and Ujinao’s grandmother and step-mother (Ujimasa’s second wife) both died mysteriously on the same day. Historians generally believe they committed suicide, either in protest of a peace deal or in prospect of one.
News of the fall of other fortresses was followed by the public display of the heads of those killed, and then the wives and children of the survivors outside the castle walls, further depleting the defenders’ morale. Towards the end of the siege, the appearance of Ishigakiyama Castle, built in just a few months, on a mountain not far from Odawara, effectively ended what remained of the Hojo’s will to resist.
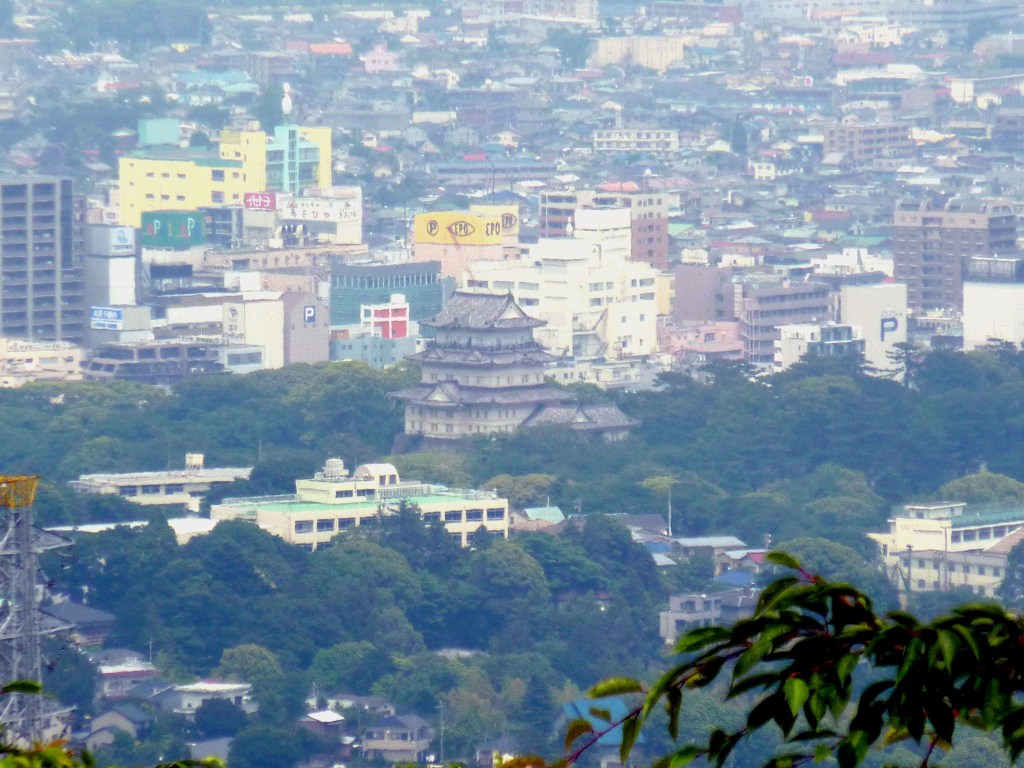

A side note here, there is a popular legend that Ishigakiyama Castle was ‘built in one night’, which was clearly impossible, with later sources suggesting that rather than literally being built overnight, the castle was instead constructed behind a forest, which was itself cut down overnight, giving the impression that the castle had appeared from nowhere. Modern scholars doubt that either version is true, as Ishigakiyama is easily visible from Odawara, and though the castle was certainly built unusually quickly, it is now thought to have been constructed in full view of the Hojo, to highlight the impossibility of their situation.
After this, the besiegers made a point of keeping up a light but continuous rain of gunfire on the castle, intending to grind down their morale, and when a final, furious night attack from the castle was repelled in August, the writing was on the wall, and a delegation from the Hojo was sent out to offer the seppuku of Hojo Ujinao and the surrender of the castle, in exchange for the lives of the remaining garrison.
Hideyoshi accepted the surrender of the castle on the condition that all the remaining senior Hojo, Ujinao, his father Ujimasa, and uncle Ujiteru, commit seppuku, and that the provinces of Musashi, Sagami, and Izu (the Hojo heartlands) be given up. Further resistance was now impossible, and the Hojo agreed. Tokugawa Ieyasu successfully intervened for the life of his son-in-law, Ujinao, but he would fall sick (possibly with smallpox) and die by the end of the year.

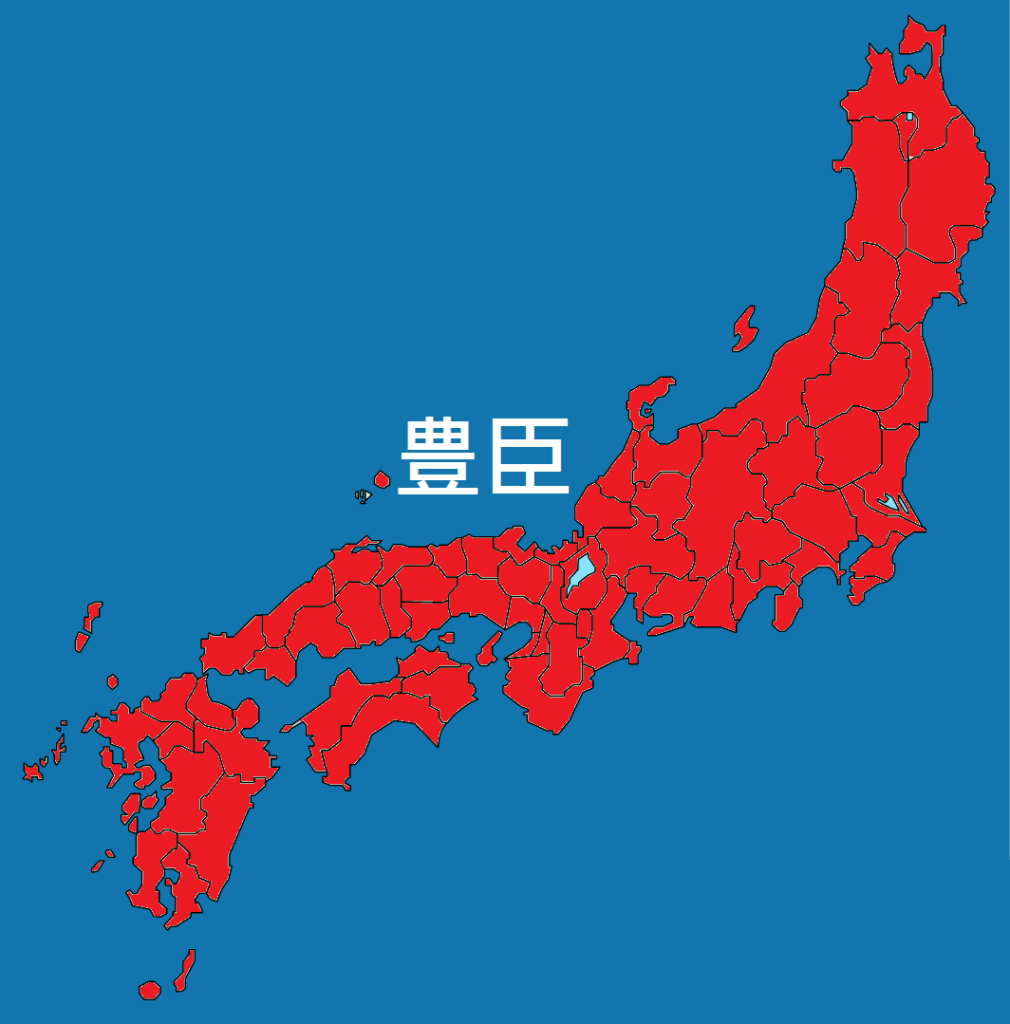
In the aftermath of the fall of Odawara, the Kanto would come under the control of Tokugawa Ieyasu, who had previously agreed to trade his three home provinces for the five of the Kanto, making his new base at Edo Castle, the site of the modern Imperial Palace in Tokyo. In the long-term, this would prove to be a genius move on Ieyasu’s part, but for now, the man who came out on top was Toyotomi Hideyoshi.
With the Hojo defeated, there were no longer any serious rivals to his rule. For the first time in more than a century, the realm was united under a single, undisputed leader, who set about ensuring it would never again fall into chaos.
By Alvin Lee – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=39214210
Hideyoshi’s conquest of Odawara marked the end of the second phase of Japan’s reunification. Next week, we’ll take a step back to look at another name we’ve mentioned a lot, Oda Nobunaga, the first of the great unifiers.
Sources
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E6%83%A3%E7%84%A1%E4%BA%8B%E4%BB%A4
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%B1%B1%E4%B8%AD%E5%9F%8E
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%B0%8F%E7%94%B0%E5%8E%9F%E5%BE%81%E4%BC%90
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E7%9F%B3%E5%9E%A3%E5%B1%B1%E5%9F%8E
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%BF%8D%E5%9F%8E%E3%81%AE%E6%88%A6%E3%81%84
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%BF%8D%E5%9F%8E
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E7%9F%B3%E7%94%B0%E5%A0%A4
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E9%A4%A8%E6%9E%97%E5%9F%8E
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%B2%A9%E6%A7%BB%E5%9F%8E
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E6%B5%85%E9%87%8E%E9%95%B7%E6%94%BF
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E9%89%A2%E5%BD%A2%E5%9F%8E
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E9%9F%AE%E5%B1%B1%E5%9F%8E
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E9%95%B7%E6%B5%9C%E5%9F%8E_(%E4%BC%8A%E8%B1%86%E5%9B%BD)
https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E6%9D%BE%E4%BA%95%E7%94%B0%E5%9F%8E
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Toyotomi_Hideyoshi
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Siege_of_Odawara_(1590)